The fall of the Roman Empire in the 5th century CE marked the end of an era and the beginning of a new world order. Numerous empires, kingdoms, and states rose and fell over the following centuries, and each of these wars had far-reaching causes, consequences, and significance in shaping the geopolitical landscape both at that time and thereafter. Here, we will explore the 17 most important wars from the fall of the Roman Empire to the present, highlighting their causes, consequences, and significance. A multiple choice test with an answer key is given at the end.
The 17 Most Important Wars in World History Since the Fall of Rome
1. Byzantine-Sassanid Wars (602–628 CE): The Byzantine-Sassanid Wars were a series of conflicts between the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire) and the Sassanid Empire (Persia) for control of the Middle East and Eastern Mediterranean. These wars had a profound impact on both empires, draining their resources and contributing to their eventual decline. The Byzantines ultimately emerged victorious, but they were left weakened and vulnerable to future invasions.
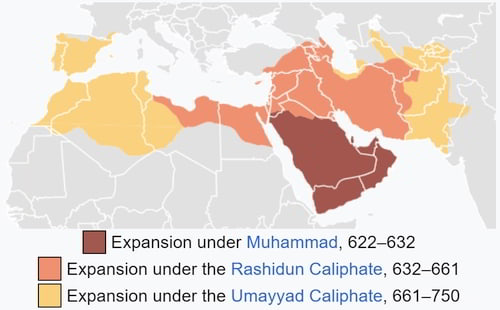
2. Muslim Conquests (622–750 CE): Following the death of the Prophet Muhammad in 632 CE, the Arab Muslims embarked on a series of rapid and extensive military conquests that established a vast Islamic empire stretching from Spain to India. These conquests had a transformative impact on the world, leading to the spread of Islam, the decline of the Byzantine and Sassanid empires, and the emergence of new cultural and political entities. The rise of Islamic empires and states was a result of the military conquests, trade, pilgrimage, and missionary activities of the Arab Muslim forces, solidifying the establishment of the Rashidun and Umayyad Caliphates and the spread of Islam over a few hundred years.
3. Crusades (1095–1291 CE): The Crusades were a series of religious wars launched by European Christians in the medieval period to recapture the Holy Land from Muslims. The objectives of the Crusades were to check the spread of Islam, retake control of the Holy Land, conquer pagan areas, and recapture formerly Christian territories These wars had a complex impact, leading to increased religious and political tension between Christians and Muslims while also fostering cultural exchange and the development of new trade routes.
4. The Mongol Conquests (1206–1405 CE): The Mongol Conquests, led by Genghis Khan and his successors from 1206 to 1405 CE, had a profound and lasting impact on the political, cultural, and economic landscape of Eurasia, leading to the spread of trade, technology, and ideas. While the conventional view portrayed the Mongol Empire as having an almost entirely destructive influence on global history, specialists have challenged this notion, asserting that the Mongols promoted vital economic, social, and cultural exchanges among civilizations. The Mongol era witnessed extraordinary developments in various fields such as painting, ceramics, manuscript illustration, textiles, agriculture, and historical writing. The Mongol invasions and conquests, which created history’s largest contiguous empire, did lead to the spread of the bubonic plague across much of Eurasia, contributing to the onset of the Black Death in the 14th century.
5. Hundred Years’ War (1337–1453 CE): This war was a prolonged conflict between England and France, stemming from English claims to the French throne. It evolved into a broader power struggle, involving factions from across Western Europe and fueled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The war saw the participation of five generations of kings from two rival dynasties, leading to significant innovations in military technology and tactics, such as professional standing armies and artillery, which permanently changed warfare in Europe. The conflict also had a lasting effect on European history, causing significant destruction and leading to the virtual destruction of the feudal nobility, thereby bringing about a new social order.
6. Ottoman-Persian Wars (1514–1736 CE): The Ottoman-Persian Wars were a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire (Sunni Muslim) and the Safavid and other Empires (Shia Muslim) for regional dominance in the Middle East. These wars had a significant impact on the political and religious landscape of the region, contributing to the rise of sectarianism and the eventual decline of both empires. The conflicts were fought over control of eastern Anatolia, the Caucasus, and Iraq, and among the numerous treaties, the Treaty of Zuhab of 1639 is considered the most important since it set the current Turkey-Iran and Iraq-Iran boundaries..
7. Thirty Years’ War (1618–1648 CE): The Thirty Years’ War was a prolonged and devastating conflict that originated as a religious war between Roman Catholics and Protestants in Germany. It later evolved into a political struggle involving various European powers, including the Catholic Habsburgs of the Holy Roman Empire, and opposing forces such as Denmark, Sweden, Catholic France, and the Protestant princes of Germany. The war resulted in widespread destruction and death, with an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians perishing due to battle, famine, and disease. The Peace of Westphalia, which concluded the war in 1648, established a new balance of power in Europe and laid the groundwork for the modern state system. The conflict is considered one of the most devastating in European history, leading to significant changes in the political and social landscape of the continent.
8. American Revolution (1775–1783 CE): The Thirteen American colonies gained independence from British authority and founded the United States of America, the first modern democracy, during the American Revolutionary War. The revolution inspired other nations to struggle for independence and promoted democracy and liberalism. British efforts to regulate colonial affairs had strained relations with its North American colonies, leading to the conflict. France and Spain joined the colonies against Britain, turning the civil war into an international war. France helped the colonies win, and the revolution’s values were founded on the American Enlightenment, promoting natural law, natural rights, consent of the governed, individualism, and liberalism.
9. French Revolution (1789–1799 CE): The French people overthrew their monarchy and established a republic founded on liberty, equality, and brotherhood. This revolution had a significant impact on France and the entire world, as it influenced French politics, society, religion, and ideas for over a century and inspired revolutions and social reforms elsewhere. The motto “Liberté, égalité, fraternité” and the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen defined the revolution. These Enlightenment ideas, which emphasized liberty, equality, and individual rights, greatly influenced the French Revolution.
10. Napoleonic Wars (1799–1815 CE): Napoleon Bonaparte’s French Empire fought a coalition of European states in these wars, which changed Europe’s political landscape and fueled nationalism and liberalism. Nationalism spread across Europe after Napoleon’s annexation and the wars, as territories objected to French rule and attempted to affirm their own identities. The Napoleonic Wars exposed the conflict between individual freedom and centralized power, which helped liberal philosophies evolve in the 19th century.
11. The Opium Wars (1839–1842 and 1856–1860 CE): The British Empire had been illegally exporting opium to China, leading to widespread addiction and social unrest. The British forced the issue by attacking Chinese port cities, leading to the weakening of the Qing Dynasty and the opening of China to Western trade and influence. The conflicts marked the start of the era of unequal treaties, which gave Western powers commercial privileges and legal and territorial concessions in China.
12. Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871): Prussia defeated France in a decisive war, leading to the unification of Germany and the establishment of the German Empire. This war had a significant impact on the European balance of power and contributed to the tensions that led to World War I. The defeat of France marked the end of its hegemony in continental Europe and the creation of a unified Germany. The conflict not only had geopolitical implications but also led to the rapid development of the modern state, influencing areas such as education and public health policy.
13. Russo-Japanese War (1904–1905): Russia and Japan fought over control of Manchuria and Korea. The Japanese victory marked the first time an Asian power had defeated a European power in a major war and helped to pave the way for the rise of Japan as a major player in world affairs. The war was known primarily for its naval engagements, and the Battle of Tsushima was the final naval battle of the war, where Japan achieved a devastating defeat over the Imperial Russian Navy. The Russo-Japanese War had significant consequences, as it accelerated revolutionary discontent in Russia and enhanced Japan’s national image as a modern state. Domestically, it had profound effects in Russia and internationally, redefining the balance of power in the Far East.
14. World War I (1914-1918 CE): World War I was a global conflict that involved all the world’s great powers and was fought between the Allied Powers and the Central Powers. The war was one of the most destructive in history, leading to a stalemate of mud and blood that lasted four long years and resulting in an estimated 9 million soldiers dead, 23 million wounded, and 5 million civilian deaths. It also led to the collapse of empires, including the Russian, German, Austro-Hungarian, and Ottoman Empires, and the rise of new nation-states such as Poland, Finland, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia. The inability to manage the post-war instability contributed to the outbreak of World War II in 1939.
15. Spanish Civil War (1936–1939 CE): The Spanish Civil War was a conflict between the Republicans and the Nationalists (fascist). The Republicans consisted of various socialist, communist, separatist, anarchist, and republican parties. General Francisco Franco led the Nationalists, who sought to overthrow the republic. The war became a proxy battleground for the major powers of Europe, with the Nationalists receiving aid from Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany and the Republicans receiving aid from the Soviet Union. The war had significant international repercussions, as it was perceived as part of an international conflict between tyranny and democracy, fascism and freedom, or communism and civilization. The fascist victory by the Nationalists helped to embolden the Axis powers and contributed to the outbreak of World War II. The war is often regarded as a “prelude” for World War II, as several of the participants in World War II, including Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and the USSR, were involved.
16. World War II (1939–1945 CE): World War II was the deadliest conflict in human history, fought between the Allied and the Axis powers. It involved over 30 countries and resulted in the deaths of over 70 million people, including about 20 million military personnel and 40 to 55 million civilians. The war led to the defeat of Nazi Germany and the Axis powers, the rise of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers, and the creation of the United Nations. The human losses during World War II were vast and had a profound impact on the course of history in the second half of the twentieth century.
17. Russian-Ukraine War (2022–Present): Russia invaded Ukraine on February 24, 2022, after President Vladimir Putin ordered a “special military operation” against the country. The invasion was the largest attack on a European country since World War II, and it is estimated to have caused tens of thousands of Ukrainian civilian casualties and hundreds of thousands of military casualties. The war is ongoing and has resulted in a refugee crisis and tens of thousands of deaths. The conflict is seen as a sign of renewed geopolitical rivalry between major world powers. The war has had far-reaching consequences, devastating Ukraine, further isolating Russia from the West, and fueling economic insecurity around the world.
Conclusion
Numerous wars that have had a significant impact on the world since the fall of the Roman Empire have marked world history. These wars shaped the political landscape, led to the rise and fall of empires, and fostered cultural exchange and innovation. By studying these wars, we can gain a deeper understanding of the forces that have shaped our world.
Multiple Choice Test on 17 Most Important Wars in World History
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question. Answer key follows the test.
- What was the primary cause of the French Revolution?
A) Economic inequality
B) Religious conflict
C) Territorial disputes
D) Ethnic tensions
- Which war led to the virtual destruction of the feudal nobility and brought about a new social order in Europe?
A) Hundred Years’ War
B) Ottoman-Persian Wars
C) Russo-Japanese War
D) Crusades
- The Treaty of Zuhab in 1639 was a significant outcome of which conflicts?
A) Napoleonic Wars
B) Byzantine-Sassanid Wars
C) Opium Wars
D) Thirty Years’ War
- What were the key ideas that influenced the French Revolution?
A) Absolutism and divine right
B) Nationalism and imperialism
C) Liberty, equality, and brotherhood
D) Mercantilism and colonialism
- Which war had a profound impact on both the Byzantine and Sassanid Empires, draining their resources and contributing to their decline?
A) American Revolution
B) Spanish Civil War
C) Crusades
D) Byzantine-Sassanid Wars
- The Russian-Ukraine War, which began in 2022, is considered a sign of renewed geopolitical rivalry between major world powers. Which major world powers are involved in this conflict?
A) China and Russia
B) United States and Ukraine
C) Russia and United States
D) Germany United Kingdom
- The Thirteen American colonies gained independence during which war?
A) American Revolution
B) World War I
C) Hundred Years’ War
D) Russo-Japanese War
- What was the primary consequence of the Mongol Conquests on the cultural and economic landscape of Eurasia?
A) Cultural stagnation
B) Spread of trade, technology, and ideas
C) Isolationism
D) Decline of agriculture
- The Opium Wars marked the start of what era in China’s history?
A) Industrial Revolution
B) Ming Dynasty
C) Unequal treaties
D) Cultural Revolution
- The Franco-Prussian War led to the unification of which country?
A) France
B) Italy
C) Germany
D) Spain
- Which conflict is often regarded as a “prelude” for World War II due to the involvement of major powers that played key roles in the later conflict?
A) World War I
B) Spanish Civil War
C) Russo-Japanese War
D) Napoleonic Wars
- Who led the Nationalists in the Spanish Civil War?
A) Francisco Franco
B) Benito Mussolini
C) Adolf Hitler
D) Joseph Stalin
- The Battle of Tsushima was a significant naval engagement in which war?
A) World War I
B) Russo-Japanese War
C) Opium Wars
D) Napoleonic Wars
- Which war involved the Ottoman Empire and the Safavid Empire in a series of conflicts for regional dominance in the Middle East?
A) Byzantine-Sassanid Wars
B) Russo-Japanese War
C) Ottoman-Persian Wars
D) Crusades
- What event marked the beginning of World War II?
A) Invasion of Poland
B) Invasion of France
C) Bombing of Pearl Harbor
D) Battle of Stalingrad
- The Peace of Westphalia, concluding the Thirty Years’ War, established what in Europe?
A) League of Nations
B) Balance of power
C) Absolute monarchy
D) Feudal system
- Which war had a profound impact on Europe, leading to the collapse of empires and the rise of new nation-states?
A) Napoleonic Wars
B) Hundred Years’ War
C) World War I
D) Mongol Conquests
- What was the primary motivation behind the Crusades?
A) Economic expansion
B) Religious goals
C) Nationalistic fervor
D) Territorial disputes
- What was the major consequence of the Russo-Japanese War on Russia?
A) Annexation of Manchuria
B) Rise of the Soviet Union
C) Accelerated revolutionary discontent
D) Establishment of a colonial empire
- The Byzantine-Sassanid Wars were fought for control of which regions?
A) Western Europe
B) Eastern Mediterranean
C) Southeast Asia
D) Sub-Saharan Africa
- What impact did the Napoleonic Wars have on Europe’s political landscape?
A) Promotion of absolutism
B) Suppression of nationalism
C) Introduction of communism
D) Promotion of nationalism and liberalism
- The Muslim Conquests led to the decline of which empires?
A) Ottoman and Ming
B) Byzantine and Sassanid
C) Roman and Gupta
D) Mongol and Inca
- Which war is often considered the deadliest conflict in human history?
A) Napoleonic Wars
B) World War I
C) World War II
D) Russo-Japanese War
- What were the primary goals of the Crusades?
A) Establishing trade routes
B) Expanding empires
C) Recapturing the Holy Land
D) Promoting religious tolerance
- The American Revolution inspired nations to struggle for independence based on which values?
A) Absolutism and divine right
B) Natural law, natural rights, and consent of the governed
C) Territorial expansion and imperialism
D) Feudalism and serfdom
- What did the Opium Wars lead to in China?
A) Strengthening of the Qing Dynasty
B) Opening of China to Western trade and influence
C) Isolation from the world
D) Cultural Renaissance
- Which conflict is perceived as part of an international conflict between tyranny and democracy, fascism and freedom, or communism and civilization?
A) World War I
B) Spanish Civil War
C) Russo-Japanese War
D) Opium Wars
- What did the Russo-Japanese War redefine in the Far East?
A) Balance of power
B) Economic systems
C) Social hierarchies
D) Military alliances
- The Treaty of Zuhab in 1639 is associated with which wars?
A) Mongol Conquests
B) Byzantine-Sassanid Wars
C) Hundred Years’ War
D) Opium Wars
- Which war contributed to the rise of new nation-states such as Poland, Finland, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia?
A) Franco-Prussian War
B) World War I
C) American Revolution
D) Napoleonic Wars
- Which conflict involved the British Empire illegally exporting opium to China, leading to the weakening of the Qing Dynasty and the opening of China to Western trade and influence?
A) American Revolution
B) Napoleonic Wars
C) Opium Wars
D) Russo-Japanese War
- The Battle of Stalingrad was a significant turning point in which major conflict?
A) Spanish Civil War
B) World War II
C) Russo-Japanese War
D) Hundred Years’ War
- What was the primary motivation behind the Crusades?
A) Economic expansion
B) Religious goals
C) Nationalistic fervor
D) Territorial disputes
- The Ottoman-Persian Wars contributed to the rise of sectarianism and the eventual decline of both empires. What were the primary regions these wars were fought over?
A) Western Europe
B) Middle East and Eastern Mediterranean
C) Southeast Asia
D) Sub-Saharan Africa
- The Peace of Westphalia, concluding the Thirty Years’ War, had a lasting impact on Europe. What did it establish?
A) League of Nations
B) Balance of power
C) Absolute monarchy
D) Feudal system
Answer Key:
- C) Liberty, equality, and brotherhood
- A) Hundred Years’ War
- B) Byzantine-Sassanid Wars
- C) Liberty, equality, and brotherhood
- D) Byzantine-Sassanid Wars
- C) Russia and United States
- A) American Revolution
- B) Spread of trade, technology, and ideas
- C) Unequal treaties
- C) Germany
- B) Spanish Civil War
- A) Francisco Franco
- B) Russo-Japanese War
- C) Ottoman-Persian Wars
- A) Invasion of Poland
- B) Balance of power
- C) World War I
- B) Religious goals
- C) Accelerated revolutionary discontent
- B) Eastern Mediterranean
- D) Promotion of nationalism and liberalism
- B) Byzantine and Sassanid
- C) World War II
- C) Recapturing the Holy Land
- B) Natural law, natural rights, and consent of the governed
- B) Opening of China to Western trade and influence
- B) Spanish Civil War
- A) Balance of power
- B) Byzantine-Sassanid Wars
- B) World War I
- C) Opium Wars
- B) World War II
- B) Religious goals
- B) Middle East and Eastern Mediterranean
- B) Balance of power
– love learning -your best ed lessons guide, Scott